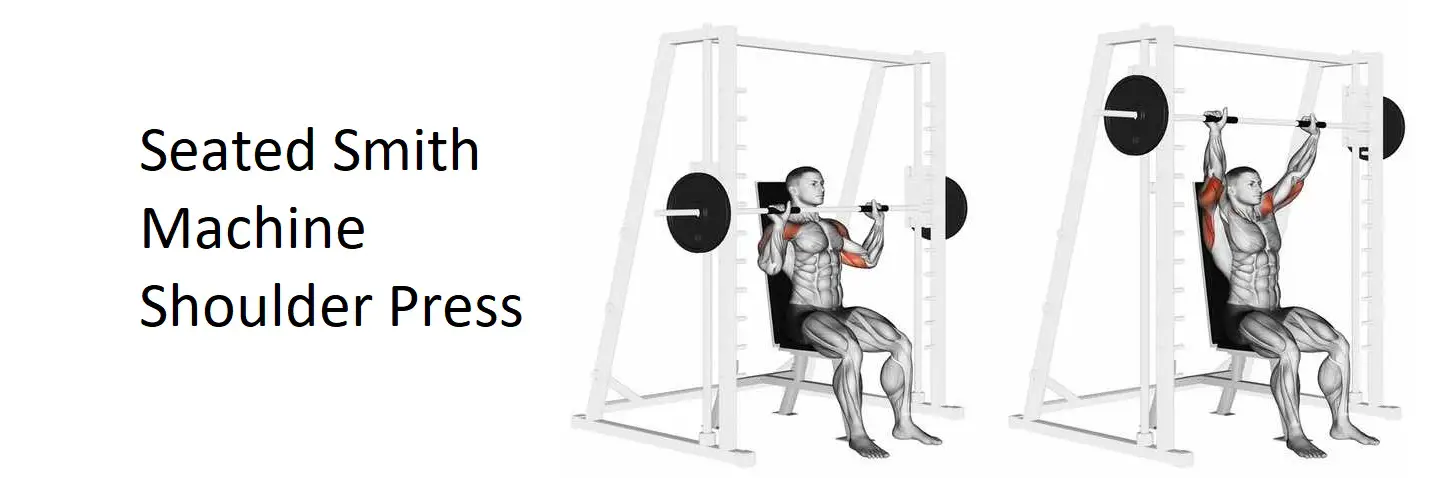
The Seated Smith Machine Shoulder Press is a compound exercise that primarily targets the shoulder muscles while also engaging the triceps and upper chest. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the correct technique, benefits, variations, and other essential details associated with the Seated Smith Machine Shoulder Press.
Instructions
Setup:
- Seat Adjustment: Sit on a sturdy bench with a backrest that provides support to your lower back. Adjust the seat height so that your feet are flat on the ground.
- Smith Machine Setup: Position the Smith machine bar at shoulder height and lock it in place. Sit on the bench with your back against the backrest and your eyes aligned with the bar.
Execution:
- Starting Position: Grip the barbell with a shoulder-width or slightly wider grip, palms facing forward. Keep your elbows bent and the barbell positioned at shoulder level.
- Pressing Motion: Exhale as you press the barbell upward until your arms are fully extended overhead. Keep your core engaged and avoid arching your back excessively.
- Peak Contraction: Pause briefly at the top of the movement, ensuring that your arms are fully extended without locking out your elbows. Feel the contraction in your shoulder muscles.
- Lowering Phase: Inhale as you lower the barbell back to the starting position under control. Keep your elbows slightly bent throughout the movement to maintain tension on the shoulder muscles.
- Repeat: Perform the desired number of repetitions with proper form and control.
Tips:
- Maintain a neutral spine throughout the exercise by keeping your chest lifted and your shoulders pulled back.
- Avoid using momentum to lift the barbell. Focus on controlled, deliberate movements.
- Keep your wrists straight and avoid excessive bending or flexing during the exercise.
Benefits
- Shoulder Strength: The Seated Smith Machine Shoulder Press is an effective exercise for developing strength and muscle mass in the deltoid muscles, particularly the anterior (front) and medial (side) heads.
- Triceps Development: The triceps muscles are also engaged during the pressing motion, helping to strengthen and develop the muscles on the back of the arms.
- Upper Chest Activation: The upper chest muscles (pectoralis major) are recruited to a lesser extent during the overhead press, contributing to overall upper body development.
- Functional Strength: This exercise mimics real-world pushing movements, making it beneficial for improving overall upper body strength and function.
Muscles worked in Seated Smith Machine Shoulder Press
The Seated Smith Machine Shoulder Press primarily targets the deltoid muscles of the shoulders, specifically the anterior (front) and medial (side) heads. Additionally, it engages several other muscles to provide stability and support throughout the movement. Here are the main muscles worked during the Seated Smith Machine Shoulder Press:
- Deltoids (Anterior and Medial Heads): The deltoid muscles are responsible for lifting the arms overhead. The anterior head of the deltoids is particularly engaged during the pressing motion, while the medial head helps stabilize the arms throughout the movement.
- Triceps Brachii: The triceps muscles, located on the back of the upper arms, assist in extending the elbows to push the barbell overhead. They work synergistically with the deltoids to complete the pressing motion.
- Trapezius (Upper Fibers): The upper fibers of the trapezius muscles help stabilize the shoulders and provide support during the pressing motion. They work to keep the shoulders in a proper position and prevent excessive elevation or shrugging.
- Serratus Anterior: The serratus anterior muscles, located on the sides of the chest, help stabilize the scapulae (shoulder blades) and assist in the upward movement of the arms. They play a role in maintaining proper shoulder mechanics during the exercise.
- Rotator Cuff Muscles: The rotator cuff muscles, including the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis, provide stability to the shoulder joint and help control the movement of the humerus (upper arm bone) during the overhead press.
- Core Muscles: The muscles of the core, including the rectus abdominis, obliques, and transverse abdominis, engage to stabilize the torso and maintain proper posture throughout the exercise. A strong core helps prevent excessive arching of the lower back and promotes overall stability during the seated Smith machine shoulder press.
Overall, the seated Smith machine shoulder press effectively targets the deltoid muscles while also engaging several other muscles of the upper body and core to provide stability and support during the movement.
Alternate names for Seated Smith Machine Shoulder Press:
- Seated Smith Machine Press
- Smith Machine Overhead Press (Seated)
- Seated Smith Machine Military Press
- Seated Smith Machine Shoulder Lift
Variations
- Seated Dumbbell Shoulder Press: Perform the exercise with dumbbells instead of a barbell to engage stabilizing muscles and address muscle imbalances.
- Standing Smith Machine Shoulder Press: Perform the shoulder press while standing to engage the core muscles and promote balance and stability.
- Push Press: Incorporate leg drive and momentum to lift heavier weights by performing a push press, which involves a slight dip of the legs before pressing the barbell overhead.
Conclusion
The Seated Smith Machine Shoulder Press is a versatile and effective exercise for developing strength, muscle mass, and stability in the shoulder muscles. By mastering the correct technique and incorporating variations into your workout routine, you can maximize the benefits of this compound exercise for overall upper body strength and function.